Kirigami-inspired solar panels
The ancient art is inspiring the design of solar cells so they can change shape to catch the sun
The rise of electric vehicles (EVs) is transforming transportation and opening new possibilities for reusing their batteries beyond their initial purpose in vehicles.
Electric vehicles have become a common sight on roads, both in urban areas and on highways. Their increasing popularity is largely driven by ongoing advancements in battery technology. Each year, manufacturers introduce models with extended ranges and faster, more efficient charging systems. However, this shift also presents challenges, particularly in managing batteries at the end of their lifecycle. Fortunately, innovative technologies are emerging to repurpose these batteries, offering them a second life.
In this article, we will explore:
Electric car batteries are the heart of these vehicles, determining key aspects such as range, charging speed, and overall durability. Over the past decade, battery technology has advanced significantly. Today’s batteries are lighter, more efficient, and have higher energy density, enabling vehicles to achieve ranges of over 400 to 500 kilometres. These improvements have alleviated "range anxiety," a common concern among potential EV buyers, and have contributed to wider acceptance of electric vehicles.
Dada la importancia de la composición química y la arquitectura interna de las baterías, resulta fundamental conocer los principales tipos que se utilizan actualmente. A grandes rasgos, podemos clasificarlas de la siguiente forma:

The recycling of electric vehicle batteries has become a critical issue for the electric mobility industry and environmental regulators worldwide. Recycling seeks to reduce the environmental impact of battery waste while recovering valuable materials, such as scarce metals and minerals. These materials can then be reused, decreasing reliance on raw material extraction and supporting the circular economy. Below are some of the most common recycling applications:
One of the most prominent alternatives for batteries that have lost capacity after thousands of charging cycles is their reuse in stationary energy storage systems, often referred to as their "second life." This approach has gained particular relevance with the growth of renewable energy sources like solar and wind, which require reliable storage solutions to manage production variability.
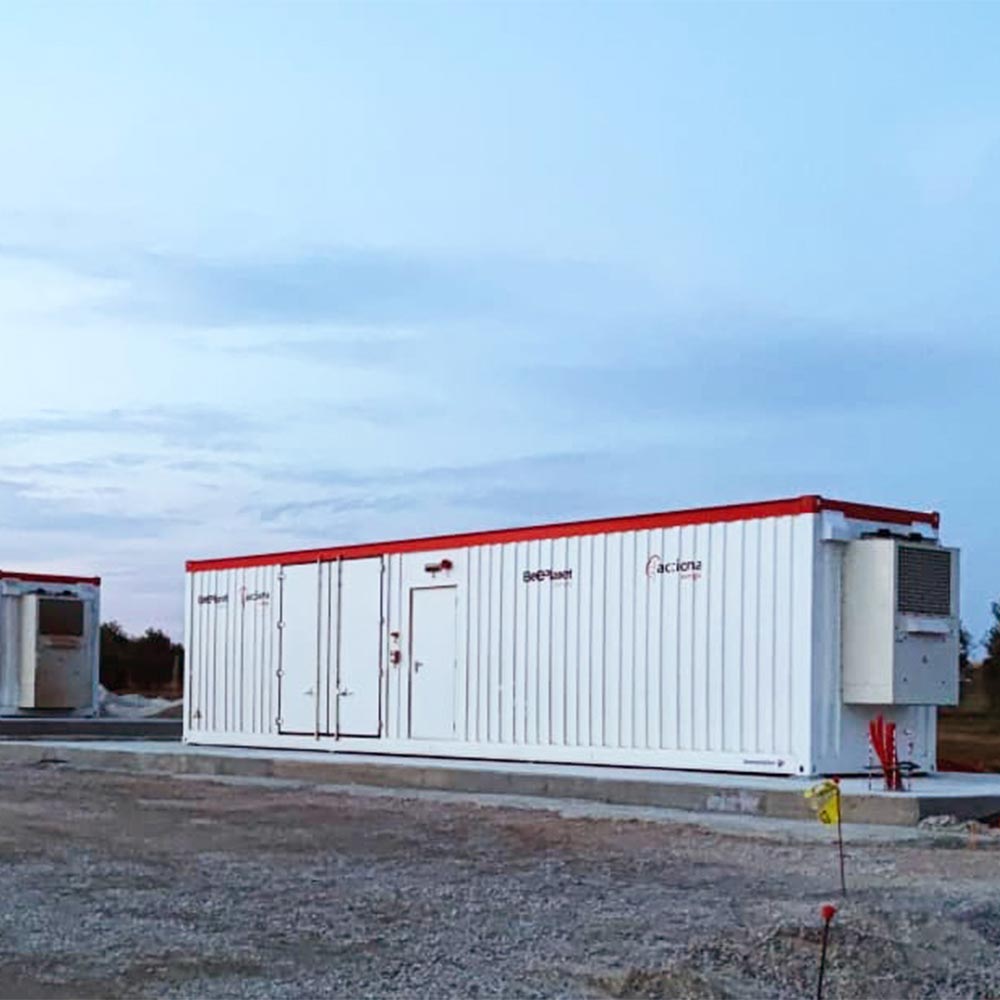
Second-life electric car batteries are commonly used to store energy generated by solar panels in residential settings or for applications like campsites. However, larger-scale projects are also being developed. One example is ACCIONA Energía's project in Extremadura, Spain.
This initiative involves a storage system at the Extremadura I-II-III photovoltaic plant near Almendralejo, using batteries mainly sourced from electric motorcycles. Notably, the site also coexists with an important archaeological area.
The storage system, classified as a Battery Energy Storage System (BESS), consists of two containers housing retired batteries with a total capacity of 2 MW/5 MWh. This system stores a portion of the energy generated by the plant and improves its integration into the power grid. As part of this pilot project, the performance and reliability of batteries from different sources are also being evaluated.
Another application for second-life EV batteries involves their use in fleets of smaller, lower-powered vehicles, such as golf carts, scooters, and electric bicycles, as well as in shared mobility initiatives in urban areas. Since these lighter vehicles have lower energy demands, batteries can remain functional for several years despite their reduced capacity.
This approach offers significant cost savings while also reducing the carbon footprint of the micro-mobility sector. Several startups and small companies are experimenting with this technology, particularly for last-mile delivery and urban transportation services. For instance, a delivery operator in Barcelona is using second-life batteries in its cargo bicycles, providing a practical example of how these systems can work in real-world settings.
When batteries degrade to the point where they can no longer power lower-demand vehicles or be used in stationary systems, they are recycled. Recycling involves disassembling the battery modules, separating the components, and extracting valuable metals and materials through chemical or mechanical processes
In Europe, regulations set specific recycling targets. By 2025, manufacturers must recover at least 65 percent of battery materials, including 50 percent of lithium and 10 percent of cobalt. These regulations aim to reduce reliance on raw material extraction and improve the sustainability of battery life cycles.
The Battery Passport is a digital traceability system that has emerged as a valuable tool in this context. It tracks the lifecycle of batteries, providing detailed information on their composition and condition. This facilitates efficient recycling and ensures the recovery of critical materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel.
Innovative companies, such as the Canadian firm Li-Cycle, are developing advanced recycling processes. These methods achieve recovery rates of over 90 percent, demonstrating the potential to significantly enhance the sustainability of battery production and use.
The recycling of electric car batteries is becoming a cornerstone of the energy transition and the circular economy. As the number of electric vehicles increases and their batteries reach the end of their useful life, developing effective and responsible waste management solutions is essential.
The environmental impact of extracting metals like lithium and cobalt, combined with the growing demand for new batteries, makes the recovery and reuse of these materials critical for the sector's long-term sustainability.
For more information on large-scale energy storage and Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS), you may find this article discussing key developments in the field insightful.
Source:
All fields are mandatory.
Read the most discussed articles
{{CommentsCount}} Comments
Currently no one has commented on the news.
Be the first to leave a comment.
{{firstLevelComment.Name}}
{{firstLevelComment.DaysAgo}} days ago
{{firstLevelComment.Text}}
Answer{{secondLevelComment.Name}}
{{secondLevelComment.DaysAgo}} days ago
{{secondLevelComment.Text}}