Nanotextures solve a historic problem
Nanotexturing that prevents scale forming on the inside of pipes can reduce plant maintenance costs significantly
Proteins produced through bacteria or bioplastics are some examples of the latest biological advances achieved by scientists.
It may remind you of viruses escaped from laboratories or amusement parks with rampaging dinosaurs. Still, the truth is that biotechnology is one of the ways to reconcile technology development and environmental protection. That is the aim at least of some of the biological scientific breakthroughs discussed in this article.
First, however, we will explain the basic concepts of biotechnology and the color codes of each of its categories, known as the biotech rainbow. Thus, in this article, we will address the following questions
In its broadest sense, biotechnology is the deliberate control and manipulation of biological systems, mainly cells or cellular components, to generate or process products and raw materials. Biotech brings together various disciplines, from physics to chemistry and mathematics, to understand the functioning of cells at the molecular scale and replicate the generation of substances and reactions by living organisms.
A basic example of biotech would be the use of bacteria to produce an electric current. These types of microorganisms are known as electrogenic and could be a source of renewable energy.
Perhaps, you may not know that our microbiota, i.e., gut bacteria, produces electricity. This type of electricity, albeit using soil bacteria, has been used to provide energy to a fishing village in Brazil. You can read the article here.
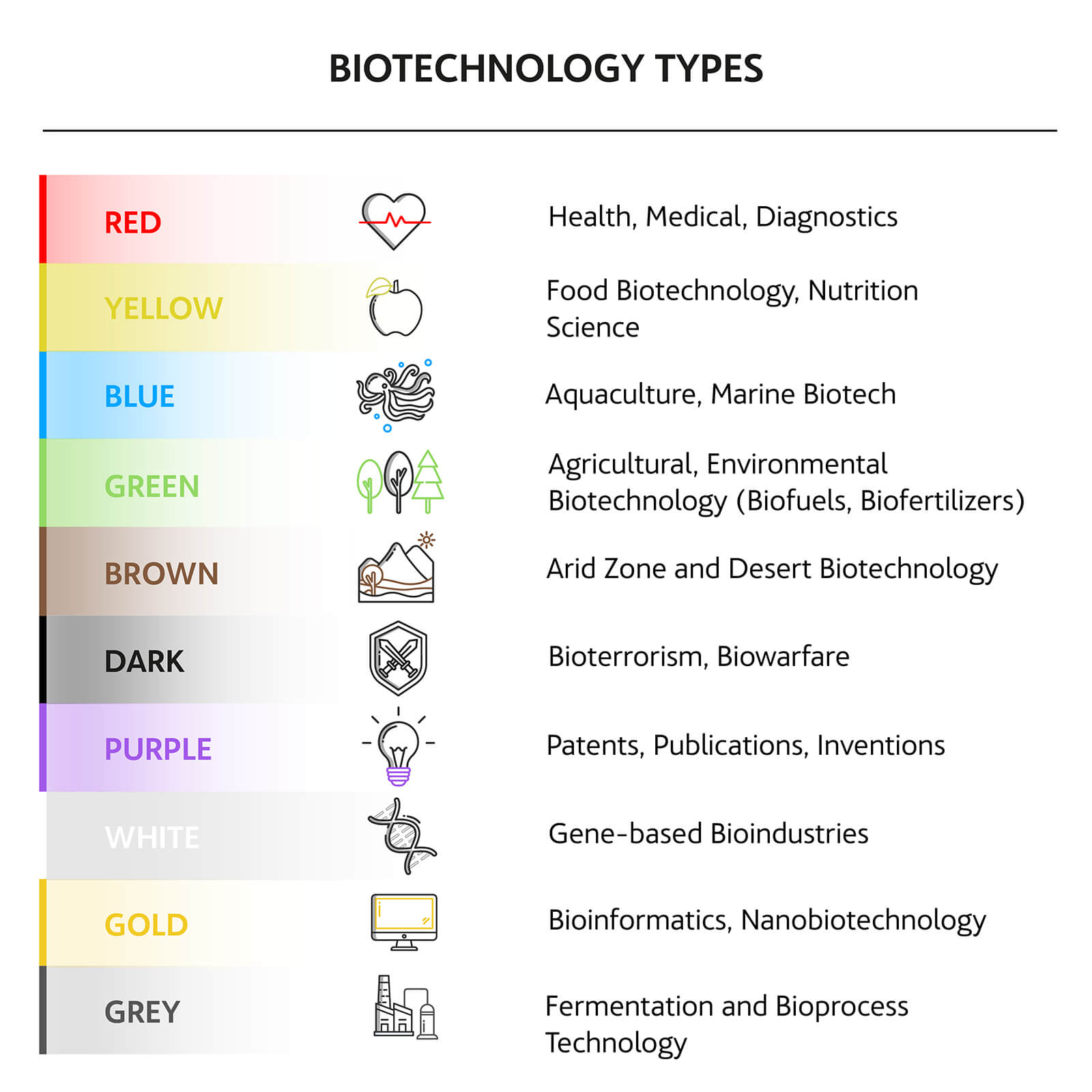
Biotechnology is a vast field that covers areas as diverse as agriculture and medicine. So much so that, officially, there are up to ten types of color codes to describe each subcategory. In the adjacent table, you can see a comprehensive classification, but the main types of biotechnology boil down to four:
The new generation of vaccines has elevated medical biotechnology to the podium of biological scientific breakthroughs. However, medical biotechnology, also known as red biotechnology, is revolutionizing areas such as organ growth from stem cells, regenerative treatments, and gene therapies. Medical biotechnology also promises to be one of the great weapons against cognitive ailments.
One of the major keys to achieving more sustainable production models involves using microorganisms such as bacteria to help us create new biodegradable materials such as bioplastics or improve the efficiency of existing processes.
Thus, white biotechnology consists of taking advantage of different cells to develop new industrial production methods.
If we want to protect the environment, reduce the use of pesticides and chemical fertilizers while also achieving more resistant and productive plants to feed the growing human population, green biotechnology is one of the few realistic alternatives. This type of biotechnology can be divided into two main areas:
1. Agriculture, mainly in crops:
2. Environment:
The seas contain some of the most critical resources for the 21st century. Caring for them to avoid repeating the mistakes made on land will be one of the significant challenges. However, with judicious use, raw materials such as microalgae could contribute to developing new biofuels or protein sources crucial to our survival as a species.
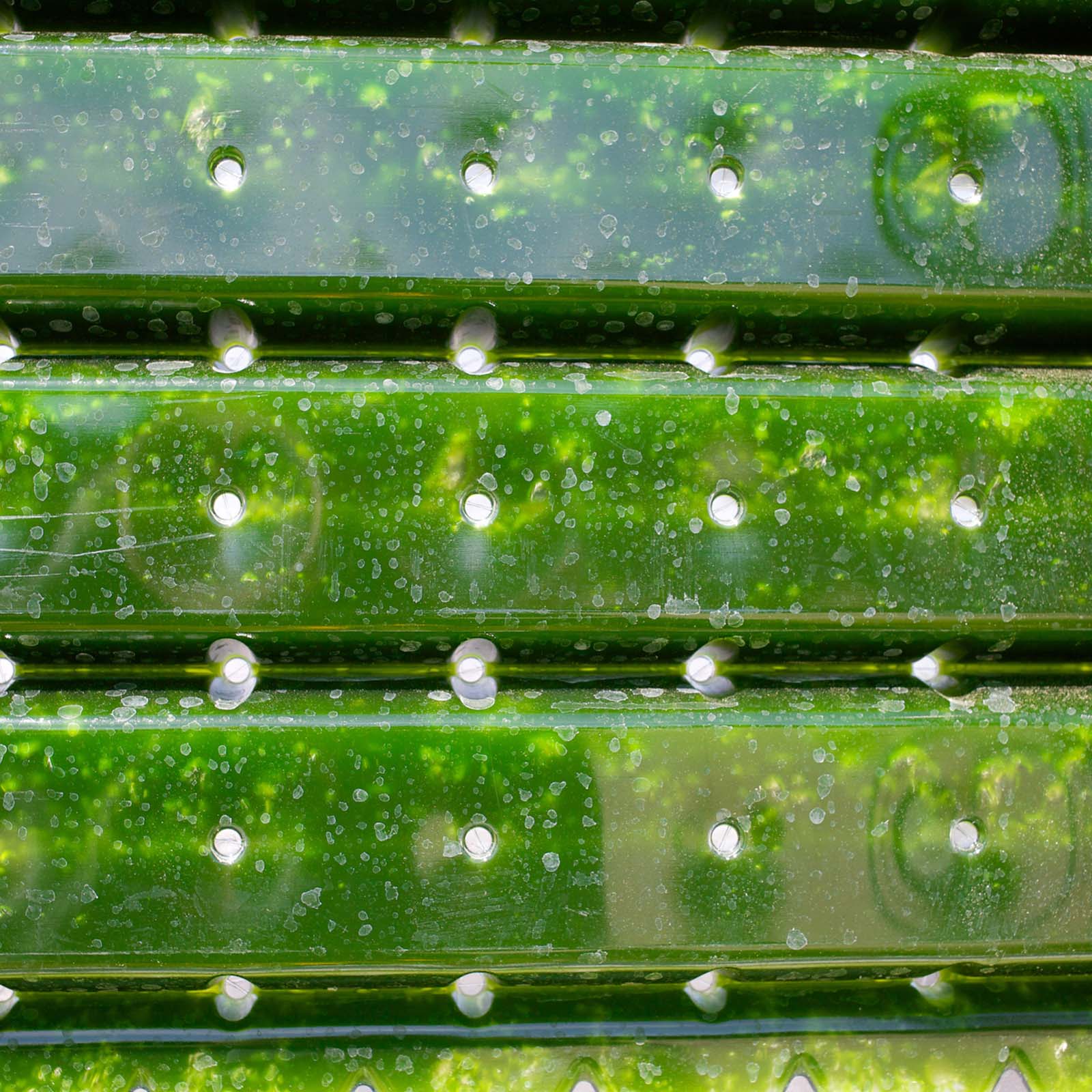

The use of algae as construction materials or raw materials for bio packaging is another promising blue biotechnology application. This potential has not gone unnoticed by supranational entities such as the European Union, which will devote the year 2022 to the blue economy.
Biotechnology is, along with nanotechnology and new materials, one of the fields where some of the most radical and fast-paced scientific breakthroughs are taking place. Therefore, it is not easy to select the most important ones. Some of the most innovative lines of research in biotechnology are:
Nevertheless, we will focus on four significant examples that show the potential of these technologies.
You might find this implausible if somebody told you that microorganisms can produce ten times as much food like plants. If, in theory, this process were carried out solely with solar energy and carbon dioxide, you would probably think it was crazy. However, that is the researchers' proposal at the Max Planck Institute for Botanical Molecular Physiology in Potsdam, Germany.
The system uses photovoltaic panels that convert water and carbon dioxide into molecules that donate electrons to microorganisms, in this case, bacteria. The microbes metabolize these molecules and generate fatty acids, carbohydrates, and proteins, among other substances.
The result may not be delicious, but it could serve as livestock food or produce protein compounds for human consumption.
Plastics and microplastics are a real environmental headache. In principle, these materials take decades or even centuries to degrade.

Fortunately, the properties of bacteria capable of metabolizing plastic are already being studied. And not only that, but the Fraunhofer Institute in Germany has also come up with another approach: using waste to generate a new type of biodegradable bioplastics.
The waste involves industrial fats with a high proportion of minerals. The German scientists have chosen to use genetically modified bacteria to metabolize the waste. The result is a biopolymer called polyhydroxy butyrate (PHB), which is extracted from the bacteria and mixed with other additives. The end product is a polyester with the particularity that it degrades within a maximum of one year when exposed to the elements.
Ten years after the disastrous Deepwater Horizon oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico, the researchers reached an exciting conclusion regarding the fate of the oil. Half of the spill had been removed by physical and chemical means. But what had happened to the other half?
The development of new genomic sequencing systems made it possible to advance our knowledge of the microorganisms in the area. Bacteria capable of metabolizing the oil and even some that devoured the chemical dispersants were found in the environment.
A study published in 2021 in the scientific journal American Society for Microbiology reveals that bacteria such as Paraperlucidibaca, Cycloclasticus, Oleispira, or Thalassolituus Zhongshania can kill pollutants in oil spills.
The test was conducted with bacteria from the Canadian Arctic. Still, scientific teams worldwide, such as the National Institute of Ocean Technology (NIOT) in India, are demonstrating the feasibility of this type of approach, known as bioremediation.
In addition to bacteria and other microorganisms, biomolecules such as proteins play a crucial role in biological scientific advances. At the Institute for Protein Design at the University of Washington, they have demonstrated the possibility of detecting coronavirus through protein-based biosensors. This new technique reveals the presence of the virus and its antibodies by emitting luminescence.
The advantage of using these biosensors is that they dispense with complex equipment required to perform PCR and similar tests. These computer-designed proteins are also being applied in biosensors for breast cancer detection.
In short, these biological scientific advances show us the potential of biotechnology to solve some of the most significant challenges of the 21st century. As we have seen, waste disposal, new renewable energies or biotherapies, and vaccines against new viruses are eloquent examples of areas where this discipline will make a difference.
Sources: Biotechhealth, The Guardian, New Atlas, ASM, Down To Earth, Eurekalert, https://explorebiotech.com/biotechnology-breakthroughs-2021/
Table: The Colours of Biotechnology: Science, Development and Humankind
All fields are mandatory.
Read the most discussed articles
{{CommentsCount}} Comments
Currently no one has commented on the news.
Be the first to leave a comment.
{{firstLevelComment.Name}}
{{firstLevelComment.DaysAgo}} days ago
{{firstLevelComment.Text}}
Answer{{secondLevelComment.Name}}
{{secondLevelComment.DaysAgo}} days ago
{{secondLevelComment.Text}}