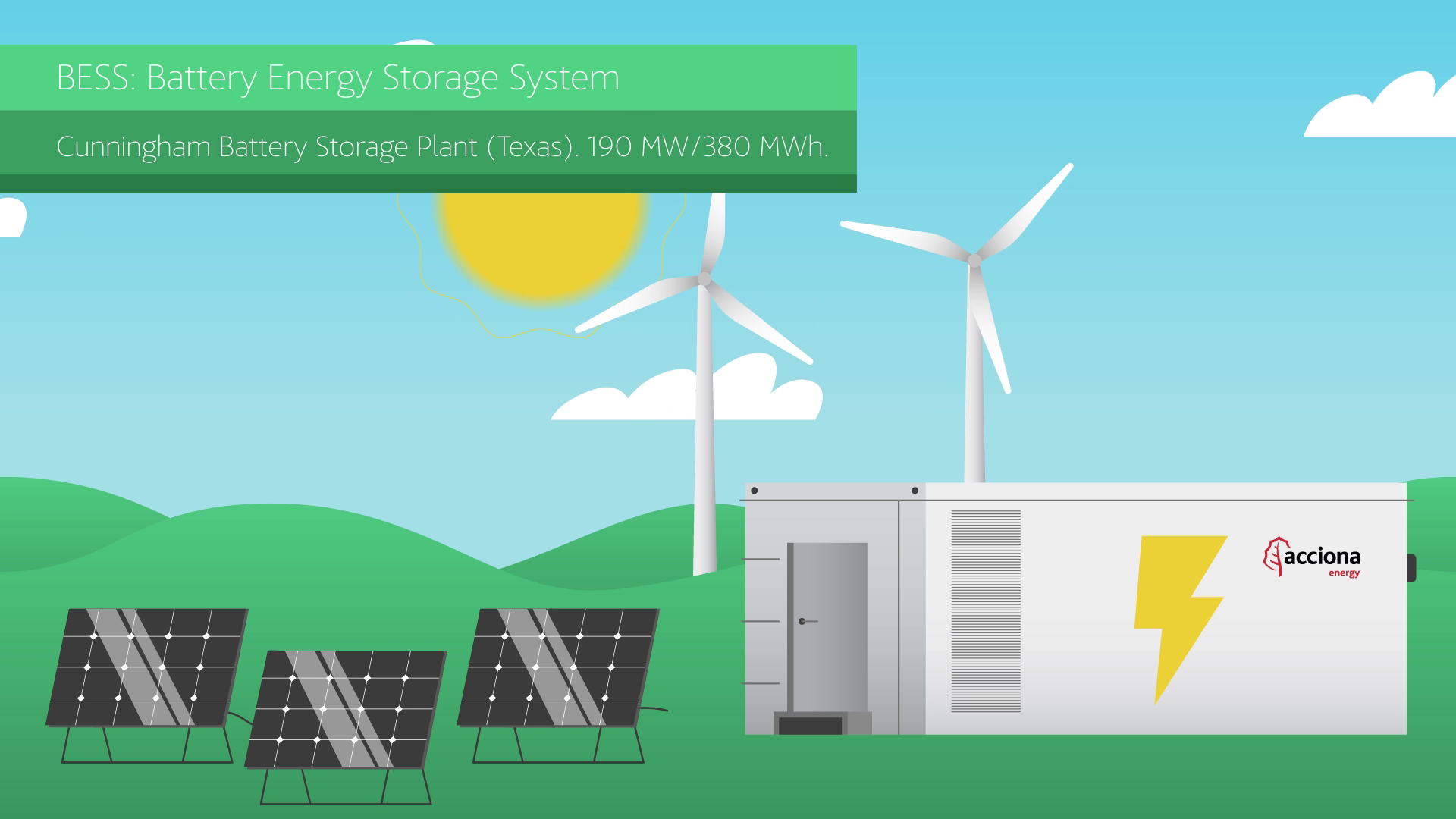
Fixed or Floating, Offshore Wind Could Be the Future of Renewable Energy
Increased wind intensity and regularity, along with low visual impact, are driving the deployment of offshore wind energy.
Turning the pitter-patter of rainfall into renewable energy is now within reach, thanks to scientific advances harnessing the kinetic power of water droplets.
Increased wind intensity and regularity, along with low visual impact, are driving the deployment of offshore wind energy.
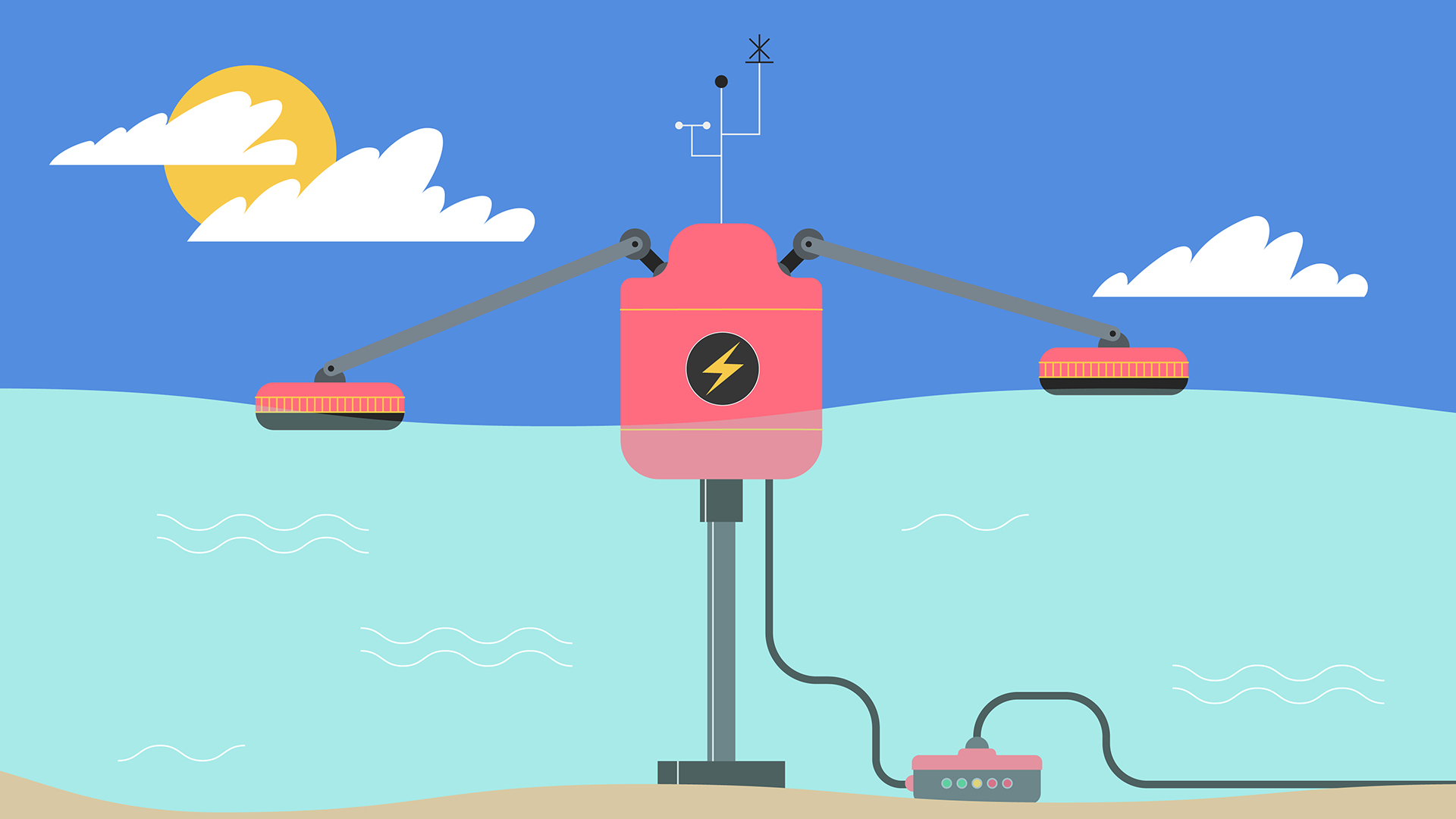
The Balearic Islands in Spain will host a pioneering project to revolutionize how we produce and consume renewable energy.
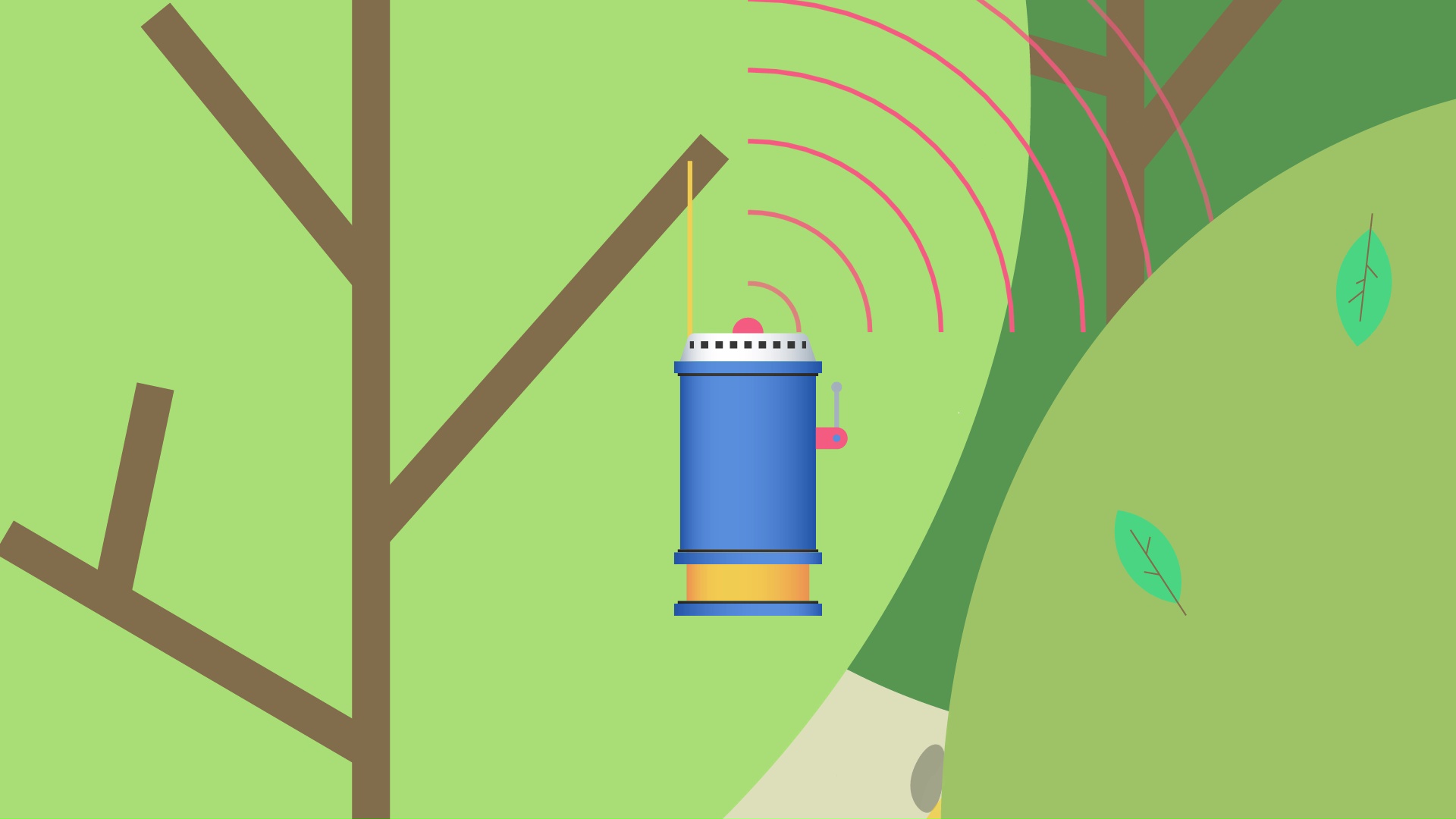
It may be low-cost and pocket-sized, but this innovative device could help power millions of IoT sensors in cities and the countryside.
An innovative technology expands the potential of solar energy to produce electricity even at night.
As a new self-consumption solution, this technology uses vibrating masts that can be installed almost anywhere.
Three types of bacteria interacting with each other form the basis of this new biobattery that could power future IoT devices.
A new type of structure will allow floating offshore wind to emerge as one of the renewable energy alternatives of the future.
Read the most discussed articles
Solar thermal energy, also called solar thermal power or thermoelectric energy, is a renewable energy that uses the heat of the sun to produce clean electricity on a large scale. Like photovoltaic energy, which uses light energy from the sun captured by solar cells, solar thermal technology uses the sun's heat to warm a fluid, produce steam, and generate electricity in a conventional thermal process. There are also several technologies used to produce thermal energy: parabolic trough and central tower, primarily.
Solar thermal energy, also called solar thermal power or thermoelectric energy, is a renewable energy that uses the heat of the sun to produce clean electricity on a large scale. Like photovoltaic energy, which uses light energy from the sun captured by solar cells, solar thermal technology uses the sun's heat to warm a fluid, produce steam, and generate electricity in a conventional thermal process. There are also several technologies used to produce thermal energy: parabolic trough and central tower, primarily.